The cost of food safety breaches and the value of prevention
Nov 14, 2024

When it comes to food safety, there is no doubt that we all want to ensure that our food is safe and nutritious. Unfortunately, food safety breaches can happen at any time – which means that they can have a significant impact on businesses and consumers alike. In addition to being costly, these types of incidents can also have a serious impact on public confidence in the safety of our food supplies. As we can see from recent high-profile cases such as the 2017's E. Coli outbreak in spinach and the 2018 salmonella outbreak linked to Kellogg's cereal, these incidents can devastate business reputations. They can even affect consumer confidence in the entire food industry.
In the US alone, it is estimated that approximately 48 million people fall ill due to food poisoning every year - resulting in billions of dollars in medical expenses and lost productivity yearly. It is also estimated that the annual cost of these illnesses is estimated at more than $100 billion! Considering this, it is no surprise that companies are keen to do everything in their power to prevent outbreaks from occurring in the first place.
But what is the real cost of an outbreak? And what value do preventative food safety measures offer compared to reactive approaches?
In this blog article, we will explore how the cost of a food-borne illness outbreak is calculated and examine the potential benefits that preventative measures can bring to businesses.

According to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the estimated cost of food-borne illness in the US is between $152-$180 billion dollars per year.
- This estimate includes direct medical costs incurred by patients and indirect costs such as lost productivity and administrative expenses. However, it should be noted that these figures only consider costs associated with illnesses documented by healthcare providers. Therefore, they will likely underestimate the cost of outbreaks as not all cases are reported.The figures above do not consider the increased safety risks that may arise if an outbreak is not quickly identified and contained. For example, in the case of an outbreak of Salmonella in tomatoes, the FDA was forced to recall millions of cases of the affected produce to contain the spread of the disease. As a result, the company had to divert staff from other tasks to focus on containing the outbreak. This resulted in an estimated loss of $53 million for the company.
- While no lives were lost due to the outbreak, thousands of people were affected by the disease, which can have lasting consequences for the victims, their families, and communities. By investing in preventative measures, companies such as Campbell’s were able to prevent costly outbreaks of food-borne illnesses and reduce the burden on healthcare resources.
In many cases, the costliest part of an outbreak is the time and resources required to contain it. This is true for the companies that experience an outbreak and the health authorities tasked with containing it. Unlike conventional medication where the active ingredient can be easily isolated and identified, food is a complex mixture of many different ingredients. This can lead to lengthy and time-consuming investigations to identify the source and prevent the further spread of the disease.
In addition, early detection of an outbreak of food poisoning helps to prevent the illness from spreading to consumers who were not exposed to the initial contaminated product. This can significantly reduce the resources and time needed to identify and contain the outbreak's source.
Companies need to invest in preventative measures to help reduce or eliminate the risk of outbreaks and their associated costs. This will result in significant savings for companies and help to ensure that consumers are protected from the harmful effects of food-borne illnesses.
These are five ways we can prevent food safety breaches:
- Proper food handling and storage: This includes keeping food at the correct temperatures, separating raw and cooked foods, and using clean utensils and surfaces to prepare food.
- Regular sanitation and cleaning: This includes regularly cleaning and sanitizing all surfaces, equipment, and utensils used in food preparation, as well as regularly cleaning and sanitizing the facility as a whole.
- Employee training and education: This includes training employees on proper food handling and sanitation procedures, as well as educating them on the importance of food safety and the potential risks associated with food safety breaches.
- Regular inspections and monitoring: This includes regular inspections by government or industry officials to ensure that food safety standards are being met and monitoring of food preparation processes to ensure that they are being followed correctly.
- Implementing a food safety management system: This includes implementing a system such as HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) to identify and control potential food safety hazards throughout the food production process. This system also includes regular monitoring, documentation and record-keeping, and corrective action when necessary to ensure that food safety standards are met.
In conclusion, food safety is an important issue affecting businesses and consumers. Outbreaks of foodborne illnesses can be costly, both financially and in terms of lost productivity and public trust. The cost of an outbreak can be calculated in terms of direct medical expenses and indirect costs such as lost productivity and administrative expenses. Still, these figures likely underestimate the true cost of outbreaks. Companies can take preventative measures to reduce the risk of outbreaks and the associated costs, such as investing in early detection and containment strategies. By taking these steps, companies can save money and protect consumers from the harmful effects of food poisoning.
Gerardo Fernández, Ph.D.in Biology.
Science Consultant at GoHACCP, dedicated to ensuring the safety and quality of food for consumers and manufacturers through scientific expertise and research.

What food requires a HACCP plan?
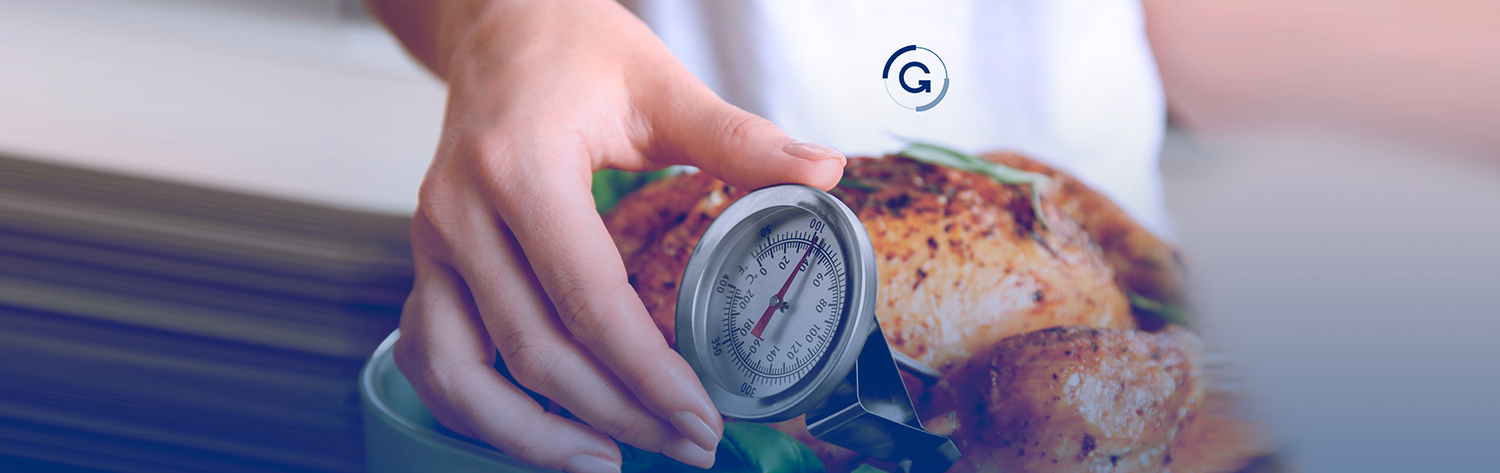

Temperature measurement is a critically important key to food safety

What are the primary food safety issues?
Join our Food
Safety Community!
Stay ahead of the curve by exploring emerging
trends and technologies in food safety.

